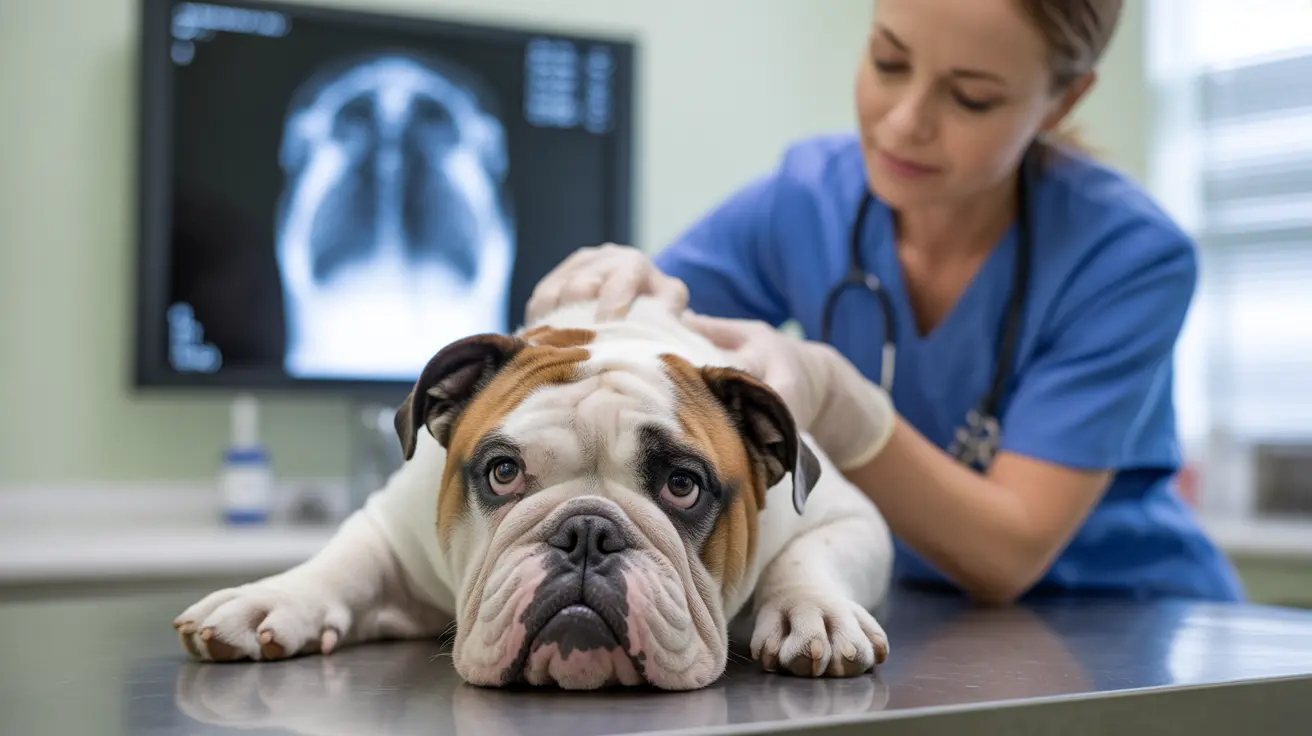
The bulldog skull is one of the most distinctive and recognizable features in the canine world. Its unique structure, characterized by a shortened face and broad head, makes bulldogs instantly identifiable but also contributes to various health challenges. Understanding the anatomy of a bulldog's skull helps us better comprehend both their appealing characteristics and the medical considerations that come with this distinctive breed.
The Unique Architecture of the Bulldog Skull
Bulldogs belong to a category of dogs known as brachycephalic breeds, characterized by their shortened skull structure. The most notable features include an extremely shortened muzzle, a wide and square-shaped head, and an upturned nose. This distinctive anatomy results from centuries of selective breeding that has dramatically altered the natural canine skull structure.
The skull's width often exceeds its length, creating that characteristic broad-faced appearance that bulldog lovers adore. The forehead is typically wrinkled, and the jaw structure frequently results in an underbite, where the lower jaw extends beyond the upper jaw.
Anatomical Components and Features
The Brachycephalic Structure
The brachycephalic skull formation includes several key characteristics:
- Compressed facial bones
- Shortened nasal passages
- Wide-set eye sockets
- Altered jaw alignment
- Modified tooth positioning
Dental and Jaw Configuration
The compressed nature of the bulldog's skull often leads to unique dental arrangements. The teeth may appear crowded or misaligned due to the shortened jaw space. This structural characteristic can lead to various dental health challenges that require special attention from both owners and veterinarians.
Health Implications of the Bulldog Skull Structure
The distinctive skull shape of bulldogs, while endearing, can lead to several health concerns:
Respiratory Challenges
The shortened nasal passages and compressed facial structure can result in breathing difficulties, particularly during exercise or in hot weather. This condition, known as Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome (BOAS), affects many bulldogs and may require medical intervention.
Dental Issues
The crowded teeth arrangement can lead to increased risks of dental disease and infection. Regular dental care becomes particularly crucial for maintaining oral health in bulldogs.
Modern Understanding and Care
Advanced veterinary medicine has developed numerous ways to address health challenges related to the bulldog's skull structure. From surgical interventions to specialized dental care protocols, modern veterinary practices help ensure these beloved dogs can live comfortable, healthy lives despite their unique anatomical features.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do bulldogs have breathing difficulties due to their skull structure?
Bulldogs experience breathing difficulties because their shortened skull structure results in compressed nasal passages and airways. This compression, combined with an elongated soft palate and narrowed nostrils, restricts airflow and makes breathing more laborious.
How does the brachycephalic skull shape of bulldogs affect their dental health?
The compressed jaw structure often leads to overcrowded and misaligned teeth, increasing the risk of dental problems like tooth decay and gum disease. The shortened space can make proper dental cleaning more challenging.
What are the most common health problems associated with a bulldog's skull shape?
The most common issues include breathing difficulties (BOAS), dental problems, eye issues due to shallow eye sockets, and potential overheating due to inefficient cooling through panting.
Can bulldogs undergo surgery to correct breathing issues caused by their skull structure?
Yes, various surgical procedures can help alleviate breathing difficulties in bulldogs. These may include widening nostrils, shortening the soft palate, or removing excess tissue in the throat.
How does selective breeding influence the development of brachycephalic features in bulldogs?
Selective breeding over many generations has emphasized the flat-faced appearance, gradually leading to more extreme brachycephalic features. This artificial selection has resulted in the distinctive skull shape seen in modern bulldogs.
Conclusion
The bulldog's skull structure represents a fascinating example of how selective breeding can dramatically alter natural anatomy. While their unique appearance has made them beloved pets, understanding the health implications of their skull structure is crucial for proper care and management. With appropriate veterinary care and attention to their special needs, bulldogs can live happy, healthy lives despite their anatomical challenges.